Name of Skill
Release Management
Classification of Skill
Release Management is a technical skill which has to be acquired by learning and
practising. It is further classified as a management skill, or one of the
electives of management. Release management skills equip the Release managers
with necessary management skills for implementing and managing release processes
for code through development, test and production. This is often referred as
Release Management lifecycle.
The release Management lifecycle starts when the release manager receives a
request for change or a new features. During this entire lifecycle, managers are
responsible for scheduling, coordinating and management of releases across the
enterprise for multiple applications across various portfolios, there will be
multiple stakeholder, multiple tasks, multiple milestones, and all these
entities can be managed by the Release manager using proper management tools and
management skills. Skills for effective management of a project releases(PMI,
2019) are:
Communication skills
Leadership skills
Organization skills
Management skills
Technical Skills (Software Engineering)
Problem solving skills
Knowledge on Project Management methodologies (PMBOK /Prince)
Conflict Management skills
Research skills and Policy knowledge
It can be said that Release management is a parent skill, with multiple child
skills.
Prerequisites for Skill
Conventionally, there are no defined pre-requisites for Release management as a
skill, and there are no mandates related to release management, which the
release manager should have. However, in order to gain expertise in release
management, a person should be well versed with the domain. As a major
pre-requisite he/she should have a complete understanding the software
development lifecycle (SDLC) (Boyde, 2014). This is will help him/her to
understand the project phases and will be helpful in planning and integrating
the different project phases. Ideally, he/she should have executed software
development project as team member or might have managed a project as iteration
manager or project manager.
Having these pre-requisites will definitely help to manage a software
engineering project as a whole. Another key prerequisite will be knowledge of
ITIL processes (Thakur, 2018). This involves change management process, incident
management process and problem management process. These processes are often
used in different phases of the project. For example, integrating a application
module into a live environment will require the release manager to schedule a
change, and then perform the integration. If the integration fails, then he
might have to look into problem management. So, without proper knowledge of ITIL
processes these activities will be difficult to implement.
Related Software Engineering Area(s)
Release management is a subset of Project Management and also it’s a part of
Change Management that deals with inherent turbulence of software engineering.
Even though the SDLC defines the development of a software product, its
implementation is still dependent on the project management methodologies.
Typically, this is done through planning, execution, monitoring and control.
Moreover, software is an intangible product, and it is important that the
developed project meets the requirements of the clients. Typically, the clients
requirements changes as the project progress thereby introducing release
managers to solve the problem.
Rationale for Skill
In case of software engineering, Release management is a glue that holds all the
key aspects of SDLC together, including business and functional requirements.
There quite a number of reasons on why release management skills are essential,
or why a dedicated release manager is required to manage the project releases
(Ahmed, 2016). Some of the key reasons are:
Understanding the differences between a change and release : Change
and Release Management sit in the transition stage of ITIL lifecycle [9].
Change represents the addition or modification or removal of anything from
the product/project whereas Release is collection of hardware, software,
documentation, processes and other components required to implement
requested change.
Standardizing Releases : Release Management helps in standardizing
and streamlining the development and operations process, the team creates a
repository for all the releases throughout the lifecycle with auditable
release controls. A single, well-documented process will increase the
organizational maturity.
Processes and policies:As the project progresses, different anomalies
will be detected. These anomalies must be analysed, and some actions have to
be performed. The release managers have to take those actions by making
policies and procedures.
Schedule Development : Development of a software product is a time
bound activity, as the product needs to be delivered to the client within a
specified deadline. The release manager has to develop forecasting skills to
create the project schedule
Development of project plan and process : Software development is
done in multiple phases/ releases and without a proper plan integrating the
phases will be difficult. There should be a clear plan, along with the
process to integrated each of the phases into a single project.
Quality Control: Release manager ensures the product is developed as
per the acceptance criteria and metrics document in Scope of Work (SOW).
This ensures complete quality control.
Roles for Skill
Release Management applies to various industries, in software engineering a
software release manager and program manager looks after release management. A
Release manager is first and foremost a project manager who looks after the
software from conception to deployment.
Monitoring the progress to ensure the release of applications are on time
and in the budget of estimation.
Communicating all the key project plans, changes, QA plans, scope
requirements with team.
Managing relationship between different teams and managing risks and
resolving issues that affect the scope, schedule and quality.
Creating a release schedule for all the core services and ensuring the
alignment across key partners and vendors.
Developing the automation tools and scripts to build, integrate, and deploy
software releases.
Work Related to Skill
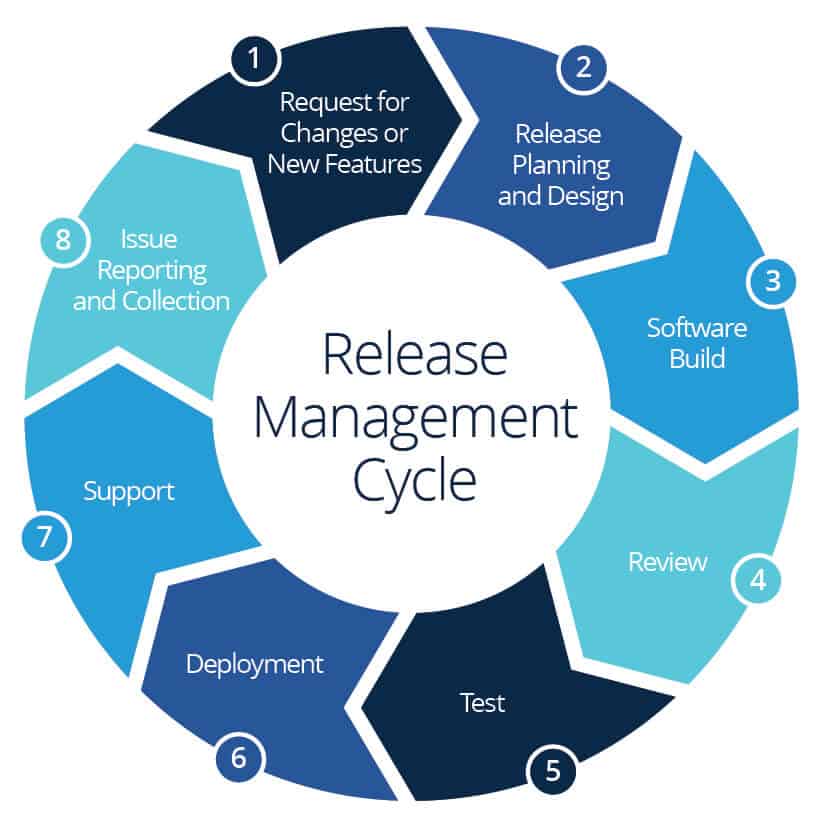
Release management follows a wee defined path, it usually begins at the first
stage of development cycle when there is a request for a change or a new
feature. Once the request is approved the release manager along with the team
design the new release and planning begins. The developers build the release,
testing takes place and modifications may be done based on the test results.
Once the release is accepted by the manager, it moves into deployment and made
available for the end users.
The following picture depicts the entire process:
The release manager needs to be well aware of all the phases of software
development lifecycle. They need know the impact of a change, how this change
affects the requirements, schedule, functional specs, development and deployment
of the release. A Release Manager must focus on automation of tasks, they have
to build processes, methods, tools and reports that help them to make decisions
whether to release a version of software or not, rather than relying on
stakeholders for every decision.
A Release Manager has to have knowledge on the following tools:
Release Management Tools : Release management involves release of the
software after development phase and test phase. Even though the release
management manages the completely development cycle, it should not be
confused with overall project management. Project management is for
management of complete project, while release management is for managing the
development at each and every stage. A project manager needs to be aware of
ITIL processes, SDLC and release management tools.
Test Case Management tools : Even though test cases are managed by
the testing team, usage of test case management tools can automate the
testing phase and make it more effective, completing the test in a shorter
span of time. Even though the release manager will not be performing any
testing, he/she needs to collect the metrics for testing, information about
test components, documentation about test assets, and defect management, and
integrate these details into the project report. That is project manager
should be aware for test case management tools.
Iteration Management : In a typical software development environment,
project is refined with every iteration, unless it is not appropriate of
final delivery. In every iteration a specific feedback is developed, and the
same is shared with the development team, who incorporates in the product,
and prepares for the next iteration. The project manager doubles up as an
iteration manager and is responsible for managing all the iterations in a
typical project. This involves involving the stakeholders for each of the
iterations, collecting the data from each iteration, and sharing the output
with the stakeholders.
Real-World Example
As most of the software moved into Software as a Service (SaaS) model, the
release management has become a vigorous process. Especially in the case of
business which have far more changes and feature request that has continuous
delivery pipelines.
In order speed up the delivery process, release managers use release management
tools like JIRA which are used create new versions of the software by reusing
the already existing versions and by automating the routine operations which are
done in each release. The following short video represent how the release
managers actually plans a each release :
Role of Academia or Industry in Cultivating the Skill
Research papers and academic books nurture the idea of elicitation.
Currently, there is a focus on the types of interviews being done, and whether
they are structured interviews or unstructured, to check which collects more
information compared to the other.
Different research papers are conducting surveys and evaluating some techniques
for eliciting requirements of computer-based systems, paying particular
attention to how they deal with social issues.
Tools Supporting the Skill
There are various tools that are available in the market for release management.
Some of the most popular tools are:
Automic: This tool automates the integration there by providing added
advantage.
BMC Release Process: This tool allows to deploy changes to the applications
with lightweight, web-based task co-ordination and execution
CA Release: This tool enables continuous delivery for agile software
development.
Micro Focus Release: This is used to manage the release management lifecycle
from development, deployment to production.
Plutora: This provides high-quality automated software through continuous
delivery management.
Urban Code Release and XL Release are some of the other tools which are used in
release management.
Skill Self-Assessment
I would rate myself as 6 on this skill. I am a team player, and I often look to
take up the responsibilities. On the other hand, I manage to finish my tasks and
assignments in time, and that is why I feel I am good at time management.
However, I am still exploring SDLC, and I lack experience in implementing a
software project, which is a definite drawback in this case. I also lack
exposure to the project management tools which is again a challenge for me. To
summarise, I have leadership qualities and interpersonal skills, but I lack
exposure to a real world SDLC and the release management tools, which justifies
the rating I have given to myself.
References
Please find below the list of references used in writing this web page:
- Boyde, J., 2014. A Down-To-Earth Guide To SDLC Project Management (2nd
Edition). New York: Springer.
- PMI, 2019. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge.
Chicago: s.n.
- PMI, 2019.Software Release Management.
- Thakur, A., 2018. The ITIL® v3 - Basics: Get to know a Successful
Project Manager. New Delhi: Springer.
- Ahmed, A., 2016. Software Project Management: A Process-Driven
Approach. Chicago: CRC Press.
- Axelos, ITIL certifications in release, control and validation
- Plutora , Release Management ‘
https://www.plutora.com/blog/release-manager-job’
- CM crossroads, What is Release Management and why we need it
‘https://www.cmcrossroads.com/article/what-release-management-and-why-it-needed’
