Planning Measurement Process By Nesar Ul Alam
Software Engineering ProcessPlanning Measurement Process is a technical skill. It mainly concerns the requirement, definition, analysis and evolution of measurement attributes. To get the best results, Planning is recommended prior to the development process so that necessary changes can be made while developing the software product. After planning the process comes the part where the plan is executed and later on improved by evolving plans as the product gets developed and there are different measurement needs.
Software Requirement Analysis is needed to gather information for the project and to identify the metrics needed to measure. The first part of the planning is to identify the scope of the measurement process and to establish a plan that is on par with the project goals.
Planning is done each time a process is executed and the results are used to improve the process in the project. So, each time a process is executed the data are collected and then used to develop another improved planning process.
Measurement is an important aspect in all engineering disciplines and it is the same for Software Engineering. It is a crosscutting skill area and provides metrics that help evaluate a process, so as to improve the development process, so that minimum resources (in terms of time and cost) are used.
A well-planned software measurement process benefits an organization in several ways. For example, it allows to identify and resolve risk issues before it is there. It provides means to improve the quality of software as well as the productivity and it gives the idea whether the software process is feasible enough to meet the organizational goals.
Project Manager, Team Leader are involved in planning a measurement process.
In software development organizations, while planning for the measurement process, efficiency and effectiveness are commonly measured. This is done to understand whether the process is “doing things right” and “doing the right things”.
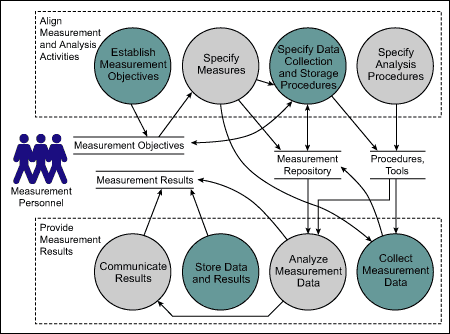
Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) is a model which serves as the baseline for software companies for improvement, productive and efficient behaviors. Measurement and Analysis is included as a Level 2 support in the CMMI[4].
In Academia research on different software metrics are still being made. This will lead to better understanding of metrics used in different aspects of Software Development Process.
Moreover, in the industry, project managers use metrics collected from past projects, which are used as the basis to understand the estimates of time and effort of the current project. So, as a software is being developed the metrics are compared to monitor and control the process. This results in better quality, less defects in the software and the amount of rework is lessened, which of course reduces the overall production cost. Therefore, metrics used to evaluate a process serves as a reference for future projects.
- Taiga
- SonarQube
- SoMeSPC
- JavaNCSS
- Microsoft Excel for spreadsheets
My Skill Score: 7/10
My knowledge on Software Measurement is based on the course SOEN 6611, where I worked on cost and effort estimation, Productivity measures and Data collection. I used JavaNCSS Maven plugin. But I would have given more score if I implemented this knowledge in a real-world software development environment.
Please find below the list of references used in writing this web page:
- SWEBOK3
- McAndrews. Donald, "Establishing a Software Measurement Process," Software Engineering Institute, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, Technical Report CMU/SEI-93-TR-016 , 1993. http://resources.sei.cmu.edu/library/asset-view.cfm?AssetID=11917/li>
- Practical Software Measurement: Measuring for Process Management and Improvement”, William A. Florac Robert E. Park Anita D. Carleton April 1997
- https://www.isixsigma.com/industries/software-it/connecting-six-sigma-cmmi-measurement-and-analysis